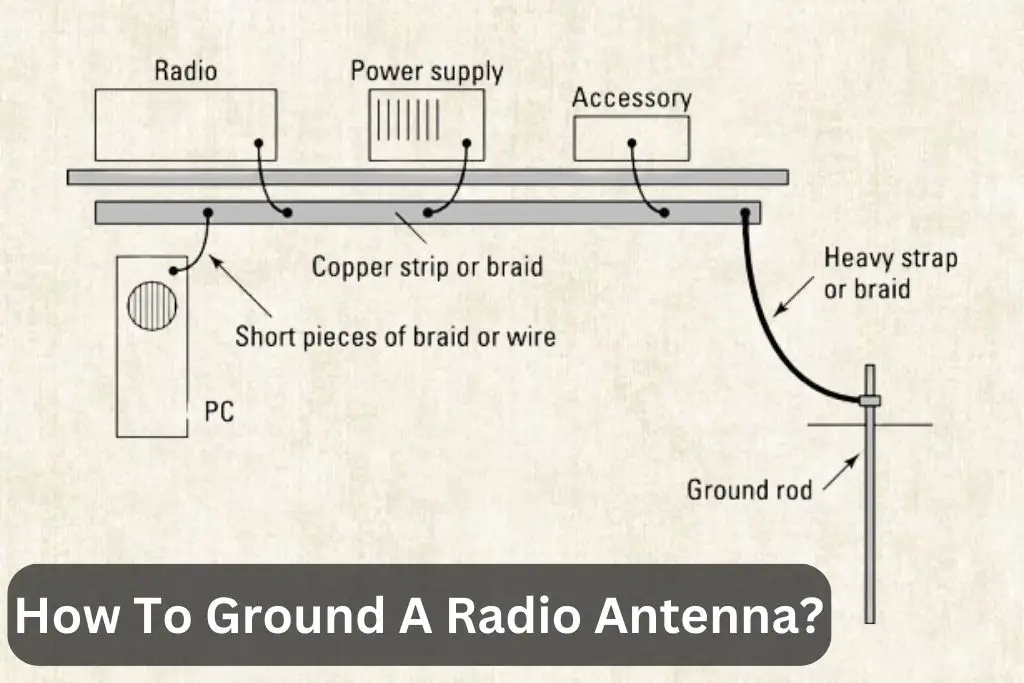
How To Ground A Radio Antenna? – Super Simple Guide 2024
Grounding a radio antenna is essential for safety and optimal performance. Proper grounding helps protect your equipment and ensures that any electrical surges or lightning strikes are safely diverted into the ground, preventing damage to your radio and other devices.
As I mentioned above, how to ground a radio antenna? In Short, To ground a radio antenna, connect a copper or aluminium grounding rod to the antenna must using copper grounding wire. Ensure a low-resistance path to Earth, driving the rod at least 8 feet deep. Bond the wire securely to the mast and ground rod, preventing lightning damage and static buildup.
Here’s how to ground a radio antenna:
- Choose a Grounding Rod: Start by selecting a suitable grounding rod, typically made of copper or galvanized steel, and ensure it’s long enough to reach deep into the earth.
- Location: Find a location near the base of your radio antenna to drive the grounding rod into the ground. Make sure it’s clear of any utility lines or other obstructions.
- Dig a Hole: Dig a hole deep enough to accommodate the grounding rod, usually 8 to 10 feet deep, depending on local electrical codes.
- Install the Grounding Rod: Insert the grounding rod into the hole until only a few inches are visible above the ground. Ensure it’s firmly in place and not wobbly.
- Connect the Ground Wire: Attach a heavy-gauge copper wire (at least 10 AWG) to the grounding rod using a ground rod clamp. People commonly refer to this wire as the “grounding conductor.”
- Run the Ground Wire: Run the grounding conductor from the rod to the base of your radio antenna. Ensure it’s securely fastened to the antenna’s mounting structure.
- Bonding: If you have multiple antennas, metal structures, or additional equipment, Ensure that bonding conductors bond everything together. This prevents potential differences in voltage between different components.
- Surge Protector: Consider installing a surge protector between your radio equipment and the antenna cable. This added layer of protection can help divert harmful surges away from your equipment.
- Grounding Block: Install a grounding block near the entry point of your coaxial cable into your house. Connect the grounding conductor to this block and your home’s electrical ground.
Inspect and Maintain: Regularly inspect your grounding system to ensure it’s intact and corrosion-free. Moisture and corrosion can reduce the effectiveness of your grounding system.
How To Ground A Radio?
Grounding a radio itself is a rare practice. Instead, it’s typically the radio antenna that needs grounding. The grounding process for radios mainly involves grounding the antenna, as discussed in the previous section. Ensure your radio is plugged into a grounded electrical outlet to prevent electrical hazards.
Electrical safety is ensured by providing a secure route for electrical currents to dissipate into the ground, minimizing interference, and protecting against lightning strikes. Grounding requirements should always be followed according to local electrical codes. Consult a professional if you need clarification.
Also Read… How Do Radio Antenna Work?
How To Ground A Ham Radio Antenna?
Grounding a ham radio antenna follows the same principles as grounding any radio antenna. Ground ham radio antennas to ensure safety and protection against electrical surges.
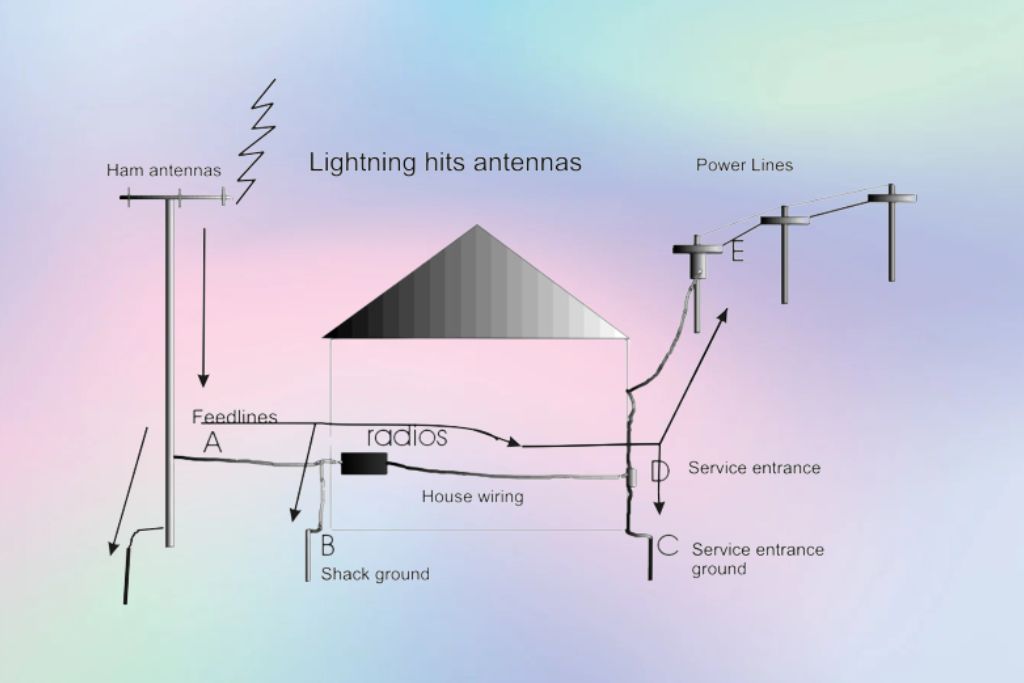
Follow the steps outlined in the section on grounding a radio antenna.
Also Read… How To Use A Ham Radio As A Walkie Talkie? – Best Info 2023
How To Ground A CB Radio Antenna?
Grounding a CB radio antenna is similar to grounding any other radio antenna—Ground CB radio antennas to protect your equipment and ensure proper functionality. Follow the steps provided in the section on grounding a radio antenna.
Does An FM Antenna Need To Be Grounded?
Yes, You should ground an FM antenna for safety and optimal performance. Grounding helps protect against lightning strikes and electrical surges. Follow the steps outlined in the section on grounding a radio antenna to ground your FM antenna.
Frequently Ask Questions
Does A Radio Antenna Need To Be Grounded?
Yes, a radio antenna, whether for AM, FM, CB, or ham radio, should be grounded to ensure safety and protect your equipment from electrical surges and lightning strikes. Proper grounding is standard practice for all outdoor antennas.
How Do You Ground An Antenna?
Grounding an antenna involves:
- Driving a grounding rod into the ground.
- Connecting a heavy-gauge copper wire (grounding conductor) from the rod to the antenna’s base.
- Ensure that you bond all related equipment together for adequate grounding.
How Do You Ground An RF Antenna?
Grounding an RF (radio frequency) antenna follows the same principles as grounding any other antenna.
Ensure the antenna and related equipment Proper grounding ensures safety and performance.
What Happens If You Don’t Ground An Antenna?
Failure to ground an antenna can result in safety hazards and damage to your equipment.
Lightning strikes or electrical surges may cause fires, equipment destruction, or pose a risk to human safety. Grounding is essential to prevent these issues.
Final Thought : (How To Ground A Radio Antenna)
Finally, I hope you know How To Ground A Radio Antenna. Properly grounding a radio antenna is crucial for ensuring the safety of your equipment and achieving optimal performance.
Following the recommended steps, you can protect your radio and related devices from electrical surges and lightning strikes.
Regular maintenance and inspections of your grounding system are vital to ensure its effectiveness over time. Always adhere to local electrical codes and safety standards when grounding your radio antenna.
Video Guide
Also Read
What Does Adam Mean In Police Code? – Police Code In 2023